From Beginner to Master: A comprehensive guide to casing connectors, covering types, parameters and installation tips
2024-06-21 17:01:35 1375
The sleeve connector usually refers to a device used for the connection and protection of wire and cable. It is mainly made of metal or plastic, with internal insulation material, can connect the ends of two or more wires and cables together, while playing a waterproof, dustproof, anti-corrosion and other protective roles. In the industrial field, casing connectors are often used for electrical connections of mechanical equipment, automation equipment, power equipment, etc. In the construction field, casing connectors are often used for electrical connections of lighting systems, air conditioning systems, security systems, etc.

Different types of casing connectors and their uses
There are a wide variety of casing connectors in different industries and applications, each type has its own specific design and use. INFINITECH lists some common types of casing connectors and their uses:
Audio tube connectors: Audio tube connectors are mainly used for the transmission of audio signals, such as connections between professional audio equipment, home entertainment systems, Musical Instruments and recording studio equipment. Common audio connectors are XLR connectors (for balancing audio signals), TRS (Tip Ring Sleeve) connectors (for headphones and unbalanced audio signals), and RCA connectors (for low-level audio signals).
Fiber optic bushing connectors: Fiber optic bushing connectors are used in fiber optic communication systems, including optical signal transmission in data networks, telecommunications networks and broadcast television systems. Common optical fiber connectors include SC, LC, FC, and ST, which provide high bandwidth and low latency data transmission capabilities.
Wire bushing connector: This connector is mainly used to protect and connect wire and cable, and is suitable for electrical wiring systems in residential, commercial and industrial buildings. Wire bushing connectors can be simple crimped or threaded connectors to connect and seal the ports of the wire against water, dust and corrosion.
Power sleeve connectors: mainly used for cable connections of high-voltage power systems, such as substations, power plants and power distribution networks. These connectors are designed to withstand high voltages and currents while providing reliable electrical isolation and mechanical strength.
Network sleeve connectors, such as RJ45 connectors, are used for Ethernet and other copper wire-based local area network (LAN) and wide area network (WAN) connections. They support data transfer rates from 10Mbps to more than 10Gbps.
HDMI tube connector: HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) connectors are used for the transmission of high-definition video and audio signals, and are commonly used in the connection between televisions, computer monitors, game consoles and other multimedia devices.
Pipe sleeve connectors: These connectors are used to connect water, gas lines, oil pipes and other piping systems, providing sealing and reinforcement to ensure continuity and safety of fluid transmission.
Coaxial cable bushing connector: Used for the connection of coaxial cables, common in cable television systems, radio communications and radar systems. Common types are BNC, TNC, N-type connectors.
Tube connector key technical indicators
When selecting a casing connector, a series of technical specifications need to be considered to ensure that the connector can meet the requirements of the specific application. Here are some key technical indicators:
Step 1: Size
-
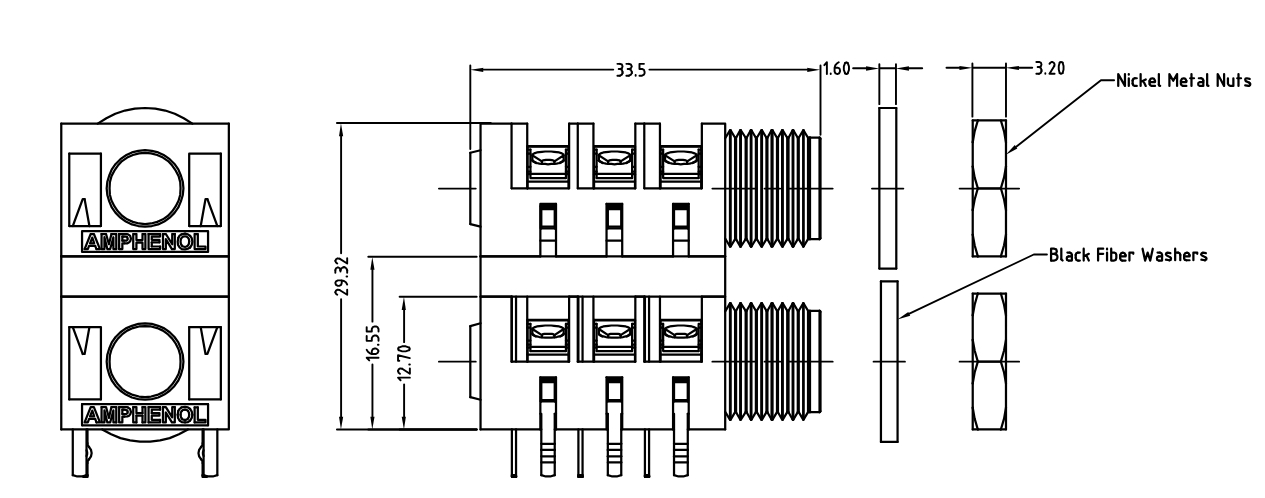
Diameter and length: Must match the size of the connected conductor or cable.
-
Thread specification: For threaded connection of casing, need to confirm the type of thread (such as M metric, NPT US taper thread, etc.) and specification.
-
Insertion depth: Ensure that the conductor is properly and securely inserted into the casing.
2. Material
-
Main material: metal (such as copper, aluminum, stainless steel) or non-metal (such as PVC, PTFE, polycarbonate PC, etc.). Metal materials provide better mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, while non-metal materials generally have better insulation and chemical stability.
-
Insulation material: Used for internal insulation, need to consider its temperature range, dielectric strength and chemical stability.
3. Electrical performance
-
Contact resistance: Low contact resistance ensures good current conduction and reduces heat and energy loss.
-
Insulation resistance: High insulation resistance can prevent leakage and short circuit.
-
Rated voltage and current: Ensures that the connector can operate safely at the specified voltage and current.
-
Capacitance: It is particularly important in high-frequency signal transmission because capacitance affects the attenuation and distortion of the signal.
4. Mechanical strength
-
Pulling force: The connector must be able to withstand a certain amount of pulling force without detaching or damaging.
-
Compressive strength: able to withstand external pressure without deformation or damage.
-
Vibration and shock: For moving or vibrating environments, connectors need to be resistant to these effects.
5. Environmental adaptability
-
Temperature range: The operating temperature range of the connector, including performance at extreme temperatures.
-
Waterproof and dust-proof rating: such as IP rating, ensure that the connector will work properly in wet or dusty environments.
-
Chemical resistance: For environments where chemicals may be exposed, connector materials need to have good chemical stability.
6. Installation and operation
-
Installation method: whether it is easy to install, such as crimping, welding, threaded connection, etc.
-
Ease of operation: whether it is easy for field operators to connect and disconnect.
7. Standards and certification
-
Compliant standards: such as IEC, UL, ISO, etc., to ensure that connectors meet international or regional safety and performance standards.
-
Product certification: Ensure that the product has passed the necessary tests and certifications, such as CE, RoHS, etc.
When selecting a casing connector, all of the above factors should be taken into account, with priority given to those indicators that most directly affect the performance and safety of the application. If it is used in special or extreme environments, it is also necessary to consider the impact of environmental conditions on the performance of the connector.
How to choose the right casing connector
Selecting the right casing connector for a specific application involves evaluating several key factors to ensure that the connector not only meets functional requirements, but also works reliably in the intended environment. The following are the main steps and factors to consider when choosing a casing connector:

1. Determine the application requirements
-
Connector type: First identify the medium that needs to be connected, whether it is power, signal, data or other. This will determine the basic types of connectors, such as power connectors, signal connectors, fiber optic connectors, etc.
-
Connector size: Measure the outer diameter of the cable or wire to ensure that the dimensions of the connector match.
-
Environmental conditions: Consider the environment in which the connector will be deployed, including temperature, humidity, corrosion, dust, and vibration.
2. Electrical performance
-
Current and voltage ratings: Ensure that the connector's current and voltage capacity is at least equal to or greater than the maximum value in the application.
-
Contact resistance: Low contact resistance helps reduce energy loss and heating.
-
Insulation resistance: High insulation resistance ensures electrical isolation and avoids short circuit.
3. Mechanical properties
-
Mechanical strength: Check the tensile strength, compressive strength and vibration resistance of the connector to ensure that it can withstand the expected physical stress.
-
Connection method: Select according to the convenience and reliability of the application, such as threading, clamping, crimping or welding.
4. Environmental adaptability
-
Protection level: Select connectors that meet the IP level to ensure that they can work under specific environmental conditions, such as water and dust.
-
Chemical resistance: For the presence of chemicals in the environment, choose a material that can resist corrosion.
5. Materials and manufacturing
-
Body material: Select materials with appropriate electrical, thermal and mechanical properties, such as metal or plastic.
-
Coating: Consider coating materials to improve electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
6. Installation and maintenance
-
Ease of installation: Choose connectors that are easy to install and remove, reducing installation costs and time.
-
Maintenance requirements: Evaluate the maintenance needs of the connector, such as whether it requires regular cleaning or replacement of parts.
7. Standards and compliance
-
Compliance with standards: Ensure that connectors comply with relevant industry standards, such as UL, CE, RoHS, etc., to meet safety and environmental requirements.
8. Cost-benefit analysis
-
Budget: Evaluate the balance between cost and performance to ensure value for money.
9. Brands and suppliers
-
Quality and reliability: Select reputable, market-proven brands to ensure product quality and after-sales service.
10. Technical support and customization options
-
Technical support: Consider technical support and solutions from vendors, especially in complex or specialized applications.
-
Customized services: If standard products do not meet the needs, find out if the supplier offers customized services.
The selection process requires close communication with engineers, technicians and suppliers in order to obtain detailed product information and technical advice.
The specific function of the adapter
Adapter is a very practical device, its main function is to solve the compatibility problem between different devices or interfaces. Adapters can convert the interface of one device into an interface that another device can recognize, allowing effective communication or data exchange between the two. The following details how the adapter implements the conversion between different types of connectors:
-
Interface conversion: The adapter can convert one physical interface (such as HDMI, VGA, USB, RJ45, etc.) to another, so that the device can be connected through different interfaces. For example, if you have a monitor with only an HDMI port, and your laptop only has a Mini DisplayPort port, you can use a Mini DisplayPort to HDMI adapter to connect the two.
-
Electrical signal conversion: Adapters can adjust the voltage and current of the power supply to suit the needs of different devices. For example, a power adapter can convert alternating current from the wall to the direct current required by the device, while adjusting the voltage and current to the appropriate level.
-
Data format and protocol conversion:
-
Data format conversion: The adapter can convert one data format to another so that different devices can understand it. For example, converting an analog signal to a digital signal, or vice versa.
-
Communication protocol conversion: Adapters can convert one communication protocol (such as RS-232 serial communication) to another (such as USB), making devices using older interfaces compatible with modern systems.
-
-
Rate conversion: When the transmission rates of two devices do not match, the adapter can adjust the data transmission rate to ensure accurate data transmission.
-
Cache and buffer: During the data transfer process, the adapter can act as a cache or buffer to ensure the smooth flow of data and avoid data overflow or loss.
-
Network adapter: A network adapter (such as an Ethernet card or wireless network adapter) can connect a computer to the network and convert data packets into the format required by the network protocol.
-
Device driver management: For adapters in computer systems, device drivers are required, which allow the operating system to communicate with the hardware adapter. The adapter may contain or require such drivers to be installed.
For example, if you have a laptop that uses Thunderbolt 3, but you need to connect a peripheral that only supports USB Type-A, you can use a Thunderbolt 3 to USB Type-A adapter. This adapter not only provides the physical conversion, but may also contain the necessary circuitry to handle the data format and signal level conversion, ensuring that the two devices can communicate properly.
Sleeve connector installation guide
Proper installation of the casing connector is essential to ensure the safety and efficiency of the system. While different types of casing connectors may have different installation steps, the following are some general guidelines compiled by INFINITECH to help you complete the installation safely and efficiently:
1. Prepare
-
Read the instructions: Read the connector's owner's manual carefully for the manufacturer's installation recommendations and warnings.
-
Check tools: Make sure you have all the necessary tools, such as wrenches, screwdrivers, wire strippers, crimps, etc.
-
Clean up the site: Ensure that the installation area is clean, tidy and free of debris to avoid contamination or damage to the connector.
2. Ensure that connectors are compatible with cables
-
Check size: Make sure the size of the connector matches the size of the cable or pipe.
-
Confirm type: Confirm that the connector type meets the application requirements, such as electrical, optical, and pneumatic.
3. Dispose of cables or pipes
-
Stripping and cutting: If using cable, properly strip the insulation to expose the conductor, but do not damage the conductor. If it is a pipe, make sure that the cutting surface is smooth and free of burrs.
-
Cleaning: Clean the ends of cable conductors or pipes with a suitable cleaner to remove grease and dirt.
4. Install the casing connector
-
Insert cable or pipe: Depending on the type of connector, insert the cable conductor or pipe correctly into the casing, ensuring that the appropriate depth is achieved.
-
Secure connection: Tighten the connector using an appropriate tool, such as a wrench or crimper, to ensure that it is securely attached to the cable or pipe. Be careful not to use excessive force to avoid damaging connectors or cables.
-
Use sealing materials: If necessary, use sealing tape, sealing paste or other sealing materials to ensure the tightness and water resistance of the connection.
5. Check and test
-
Visual inspection: Check the installed connectors to make sure there are no loose or obvious installation errors.
-
Functional testing: Electrical testing, air tightness testing or hydraulic testing as required to verify the integrity and functionality of the connection.
-
Load test: Test the connector under actual operating conditions to ensure that it can withstand the expected load.
6. Maintenance and records
-
Marking: Mark the connector or its vicinity with necessary information, such as date, test results, etc., to facilitate future maintenance and tracking.
-
Records: Keep records of installation and testing, which is important for maintenance and troubleshooting.
7. Follow safety procedures
-
Personal Protective equipment: Wear appropriate safety equipment, such as gloves, goggles, etc.
-
Power off operation: When installing electrical connectors, ensure that the circuit is disconnected to avoid the risk of electric shock.
8. Follow standards and norms
-
Compliance with standards: Ensure that the installation process complies with relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as ISO, IEC, etc.
Tip: By following these steps, you can ensure that the casing connector is installed correctly, ensuring the safety and efficiency of the system. In any case of uncertainty, it is best to consult a professional or manufacturer for advice.