Common faults of throttle position sensor
2024-11-13 15:15:05 503
Contents:
1. Introduction to the throttle position sensor
2. Common faults of the throttle position sensor
① The sensor is faulty
② The connection line is faulty
③ The ECU is faulty
④ Throttle body fault
3. Troubleshooting methods
3.1 Fault code reading
3.2 Data flow analysis
3.3 Physical Check
3.4 Signal Testing
4. Troubleshooting methods
4.1 Replacing a Sensor
4.2 Maintaining connection cables
4.3 Updating the ECU Software
4.4 Clean and maintain the throttle body
5. Preventive measures
6. Practical application cases
7. Conclusion
Throttle position sensor (TPS), as one of the key components of the automotive engine management system, is responsible for detecting the throttle opening and transmitting this information to the engine control unit (ECU), whose working state directly affects the performance and driving experience of the vehicle. Here, we will detail the common faults of throttle position sensors and their coping strategies from multiple angles, provide maintenance recommendations for car owners, and help technicians better diagnose and solve problems.
1. Introduction to the throttle position sensor

Throttle position sensor (TPS) is an important part of automobile engine management system. It is mainly used to detect the opening of the engine throttle, that is, the position change of the accelerator pedal, so as to help the engine control unit (ECU) adjust the working state of the engine to ensure that the engine can run efficiently and stably under different working conditions. It is usually installed on the throttle body. The physical position of the throttle is converted into an electrical signal via a variable resistor or potentiometer, which is then passed to the ECU. Based on these signals, the ECU adjusts fuel injection, ignition timing, and other parameters to ensure optimal engine operation.
2. Common faults of the throttle position sensor
① The sensor is faulty
Internal component damage:
The resistance or potentiometer inside the sensor may be damaged due to prolonged use or external factors (such as high temperature, vibration).
Performance: Signal distortion or complete failure, resulting in unsteady engine idle, slow acceleration, or slow engine speed rise during acceleration.
Poor contact:
Cause: The connection between the sensor and the throttle body may become loose or corroded.
Performance: The signal transmission is unstable, resulting in intermittent performance degradation or sudden stalling of the engine during operation.
Aging:
The reason: The sensor has a limited service life, and its performance will gradually degrade over time.
Performance: The output signal is inaccurate, affecting the normal operation of the engine, which may lead to decreased fuel economy and emissions performance.
② The connection line is faulty
Line break:
Cause: The connection line between the sensor and the ECU may be broken.
Performance: The signal can not be transmitted, resulting in the engine can not start or suddenly stall during operation.
Short circuit:
Reason: The connection line may be short circuit due to wear or external force.
Performance: Send wrong signals or no signals at all, resulting in abnormal engine operation.
Loose joints:
Cause: The plug connecting the line may be loose.
Performance: Poor contact or signal interruption, resulting in unstable engine operation or reduced performance.
③ The ECU is faulty
ECU software problems:
Cause: The ECU's software may have errors.
Performance: Failure to properly process signals from TPS, resulting in decreased engine performance or failure to start properly.
ECU hardware issues:
Reason: The hardware of the ECU can be damaged due to overheating, voltage fluctuations, etc.
Performance: can not work properly, resulting in the engine can not start or serious failure in operation.
④ Throttle body fault
Throttle stuck:

Reason: The mechanical parts inside the throttle body may be stuck due to carbon accumulation, dirt or wear.
Performance: The throttle cannot open and close normally, resulting in unstable idle speed, slow acceleration or inability to accelerate.
Throttle return spring failure:
Reason: Throttle return spring may lose elasticity due to fatigue or fracture.
Performance: The throttle cannot return to the closed position, causing the engine to idle too high or not close properly.
3. Troubleshooting methods
3.1 Fault code reading

The scan tool is connected through the OBD-II interface to read the fault code of the engine control system. Common TPS-related fault codes include P0121 (throttle position sensor performance fault), P0122 (throttle position sensor circuit low voltage), P0123 (throttle position sensor circuit high voltage), and P0124 (throttle position sensor signal is unreasonable). According to the fault code read and the specific symptoms of the vehicle, the cause of the fault is initially determined.
3.2 Data flow analysis
Use the scanning tool to read the data stream of TPS and observe the change of throttle opening. Compare the read data with normal values to find anomalies. For example, a sudden jump in throttle opening or signal instability can be a sign of TPS failure.
3.3 Physical Check
Check the appearance of the TPS sensor for obvious damage or corrosion, especially the housing and joint parts of the sensor. Check whether the sensor is securely installed, loose or offset.
Check that the connection line between the sensor and the ECU is broken, worn or loose and corroded to ensure that the plug connection is reliable.
Check the inside of the throttle body for carbon accumulation, dirt or wear. Check whether the throttle return spring is in good condition to ensure that the throttle can return normally.
3.4 Signal Testing
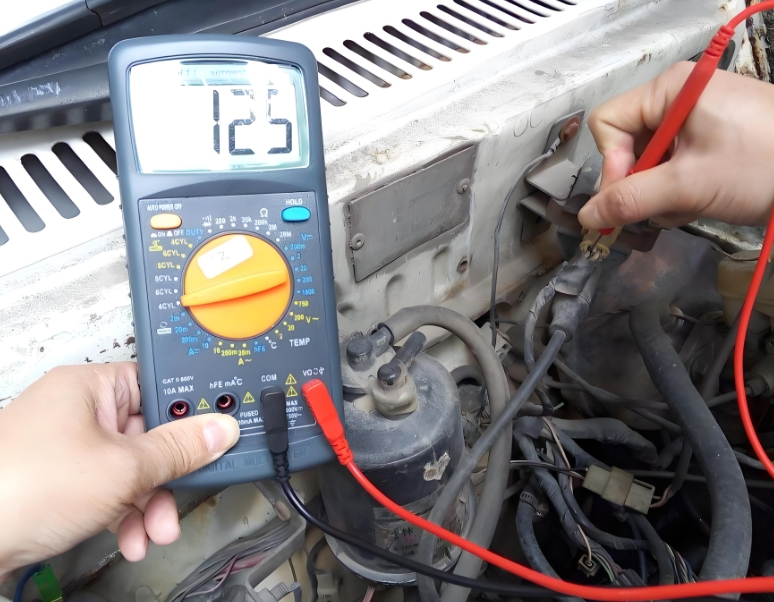

Use a multimeter to measure the resistance value or voltage value of the TPS sensor at different throttle openings and compare it with the standard value. Standard value reference: When the throttle is completely closed, the voltage is usually about 0.5V. When the throttle is fully open, the voltage is usually about 4.5V. In the intermediate position, the voltage should vary linearly between 0.5V and 4.5V.
The oscilloscope is used to observe whether the signal waveform of the TPS sensor is distorted or abnormal, such as signal mutation and noise interference.
4. Troubleshooting methods
4.1 Replacing a Sensor
After confirming that the TPS sensor is indeed faulty through the above diagnostic methods, a new sensor needs to be replaced. Select high-quality sensors that match the original vehicle to ensure compatibility and reliability. Follow the installation guide provided by the manufacturer to properly install the new TPS sensor to ensure a strong and reliable connection.
4.2 Maintaining connection cables
If the connection line breaks, it can be repaired with a wire or replaced with a new line. If the connection line shorted, you need to find the short circuit point and repair or replace the new line. If the plug connecting the line is loose, re-tighten it or replace it with a new plug.
4.3 Updating the ECU Software
Check the software version of the ECU with the OBD-II scanning tool to make sure it is up to date. If the ECU software version is too old, you can use dedicated tools to update it to ensure software stability and reliability.
4.4 Clean and maintain the throttle body
Use a special cleaner to remove carbon deposits and dirt inside the throttle body to ensure that the throttle can open and close smoothly. Check the elasticity of the throttle return spring. If the spring is tired or broken, a new spring needs to be replaced.
5. Preventive measures
To extend the service life of throttle position sensors (TPS) and ensure their proper functioning, the following precautions can be taken:

Check the appearance of the TPS sensor regularly to ensure that there is no obvious damage, cracking, or corrosion. Check the wiring between the sensor and the ECU to ensure that it is not broken, worn, or loose. Check the plugs that connect the wires to make sure they are not loose or corroded and that the pins are in good contact.
Regularly clean the carbon deposits and dirt inside the throttle body to ensure that the throttle can open and close smoothly. Special throttle cleaner can be used for cleaning. If there is dirt or corrosion on the surface of the sensor, it can be cleaned with an appropriate cleaner, but be careful not to damage the sensitive parts of the sensor.
Choose well-known brands and reliable quality TPS sensors to ensure stable performance and long life. Select sensors that comply with international or national standards, such as ISO, SAE, etc.
Select high temperature and corrosion resistant connection lines and plugs to ensure the stability and reliability of signal transmission. Select connection lines and plugs with waterproof and dust-proof functions to prevent the influence of external environment on the line.
Try to avoid parking your vehicle in direct sunlight for a long time, especially in the summer heat. Ensure that the engine cooling system is working properly to avoid engine overheating affecting the performance of the TPS sensor.
Try to avoid driving on bumpy roads for long periods of time, especially at high speeds. Ensure that the TPS sensor and its connection line are securely secured to reduce loosening or damage due to vibration.
Regularly check the running status of the vehicle, such as the engine idling instability, slow acceleration and other symptoms, should be timely fault diagnosis. Once the TPS sensor is found to have signs of failure, professional maintenance personnel should be contacted as soon as possible for repair or replacement to avoid further deterioration of the fault.
Periodically check the software version of the ECU to ensure that it is up to date for optimal performance and stability. Periodically check the hardware status of the ECU to ensure that it is well cooled and does not overheat. If the ECU is found to be abnormal, it should be repaired or replaced in time.
Avoiding frequent sharp acceleration and sudden braking can increase the load on the engine and may lead to premature damage to TPS sensors and other components. Use the accelerator properly, keep the gas pedal smooth operation, avoid suddenly pressing or releasing the accelerator, and reduce the impact on the TPS sensor.
Replace the air filter regularly to ensure that the air entering the engine is clean and reduce the impact of dust and impurities on the throttle body and sensor.
Use fuel that meets the standard and avoid using inferior fuel, so as not to affect the performance and life of the engine. Fuel additives can be used if necessary, but it is necessary to choose a reliable quality product to avoid damage to the engine.
6. Practical application cases
The engine idle speed is unstable
An owner reported that the vehicle jitter seriously when idling. The OBD-II scanning tool read the fault code and found that the TPS sensor had fault code P0121. After data flow analysis, it is found that the TPS signal is unstable. Further inspection revealed a loose connection between the sensor and the ECU. The fault was resolved by tightening the connection line and recalibrating the TPS sensor.
Acceleration weakness
Another owner reported that the vehicle was underpowered when accelerating, and read the fault code through the OBD-II scanning tool, and found that the TPS sensor had fault code P0122. After data flow analysis, it is found that the TPS signal is low. Further inspection revealed that the potentiometer inside the sensor was damaged. The fault was resolved by replacing the TPS sensor with a new one and recalibrating it.
7. Conclusion
Proper use and maintenance of the throttle position sensor is essential to ensure the proper operation of the automotive engine. As a key component of automotive electronic control system, the status of throttle position sensor directly affects the performance of the vehicle. Understanding common fault types and countermeasures not only helps improve vehicle safety and driving comfort, but also effectively reduces maintenance costs. I hope that the content of this article will provide you with useful guidance when using and maintaining throttle position sensors.