Exploring the Electronic World: Characteristics and Application Analysis of Common Diodes
2024-01-15 14:26:28 33
Diode is one of the most basic components in electronic technology and is widely used in various electronic circuits, such as amplification, detection, power supply, voltage stabilization, etc. Knowledge of the characteristics and applications of diodes is the foundation that electronic engineers and enthusiasts must master. This article will introduce the characteristics and applications of common diodes in detail to help readers understand diodes in depth.
1.Simple structure of diode
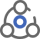
Diodes are composed of P-type semiconductors and N-type semiconductors. The majority carriers in N-type semiconductors are free electrons, and the majority carriers in P-type semiconductors are holes. When these two different types of semiconductors are combined vertically through a PN junction, a simple diode is formed.
2. Commonly used diode characteristics and identification
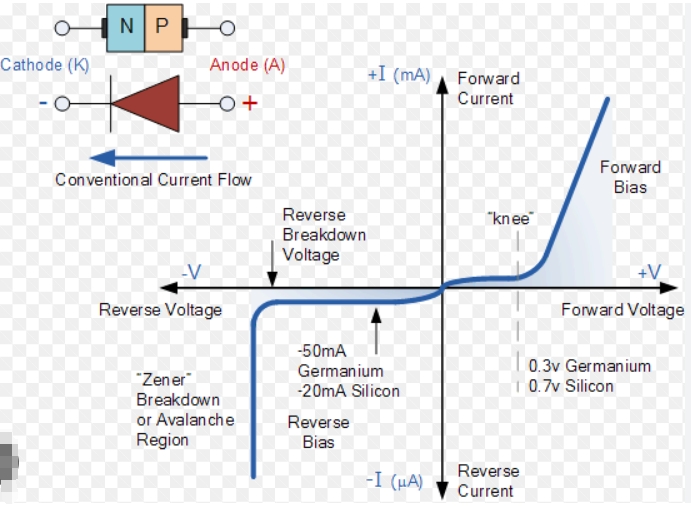
Schottky diodes
Schottky diode (Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode (SBD for short), is a low-power, ultra-high-speed semiconductor device.
The most notable feature is that the reverse recovery time is extremely short (can be as small as a few nanoseconds) and the forward voltage drop is only about 0.4V. They are mostly used as high-frequency, low-voltage, high-current rectifier diodes, freewheeling diodes, and protection diodes. They are also used as rectifier diodes and small-signal detection diodes in microwave communication and other circuits. It is common in communication power supplies, frequency converters, etc.
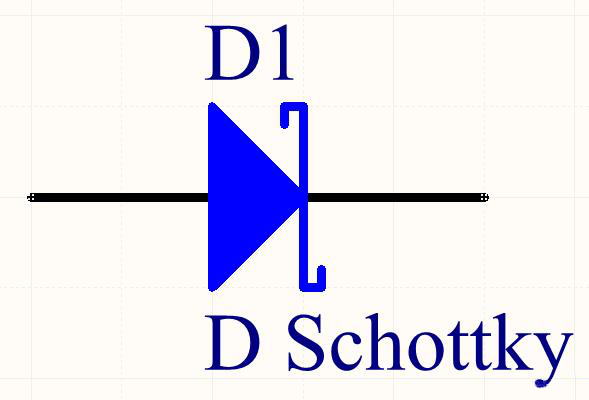
varactor diode
Varactor, also known as "variable reactance diode", is made by utilizing the characteristic that the junction capacitance changes with the applied voltage when the pN junction is reverse biased.
When the reverse bias voltage increases, the junction capacitance decreases, and on the contrary, the junction capacitance increases. The capacitance of the varactor diode is generally small, and its maximum value is tens of picofarads to hundreds of picofarads. The ratio of the maximum area capacitance to the minimum capacitance is approximately is 5:1. It is mainly used in high-frequency circuits for automatic tuning, frequency modulation, phase adjustment, etc.
Zener diode
The voltage stabilizing diode uses the reverse breakdown state of the pn junction, the phenomenon that the current can change within a wide range while the voltage remains basically unchanged, to create a diode with a voltage stabilizing function.

Ordinary diode
Ordinary diodes are one of the most commonly used electronic components. Its biggest characteristic is that it conducts electricity in one direction, that is, current can only flow in one direction of the diode. The functions of the diode include rectifier circuits, detector circuits, voltage stabilizing circuits, and various modulations. circuit.

tunnel diode
Tunnel diode, also known as Esaki diode, is a crystal diode with tunnel effect current as the main current component.
Its advantages are good switching characteristics, fast speed and high operating frequency. It is mostly used in some switching circuits or high-frequency oscillation circuits.
led
Light-emitting diodes can radiate visible light when electrons and holes recombine, so they can be used to make light-emitting diodes.
Infrared receiving diode
Infrared receiving diodes are also called infrared photodiodes.
3. Application of diodes
- Rectifier: Diodes are most commonly used as rectifiers in passive components. They quickly convert alternating current to direct current, providing stable power for a variety of applications.
- Signal Modulation: In radio transmission, diodes are often used to modulate the signal to create an effective medium through which it can be transmitted.
- Amplifiers: Diodes act as amplifiers and play an important role in television signal processing and radios. They enhance the signal by expanding the frequency range and reducing the rate of waveform distortion.
- Light-emitting diode (LED): LED is a diode that emits light by emitting light from a semiconductor material. It works without electrodes and provides an efficient, low-power lighting solution.
Through the introduction of this article, I believe that readers will have a clearer understanding of diodes, and I also hope to encourage readers to continue to learn more about diodes and other electronic components.
Tip: Whether in simple power supply conditioning and filtering schemes or as modulators and demodulators in radio transmissions, diodes play a key role in a variety of electronic applications. When dealing with diode-related issues, pay attention to the specific characteristics and usage scenarios of the components to ensure efficient design and implementation of the circuit.