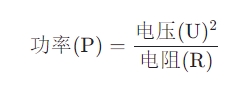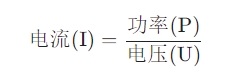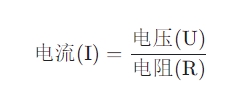Electric heating tube type and working principle, power calculation
2024-04-12 14:00:25 96
Electric heating tube is a common electric heating element, mainly used to convert electrical energy into heat energy to achieve direct heating of fluid, solid or gas medium. Its design principle is based on the principle of resistance heating, that is, when the current passes through a material with a certain resistance value, it will generate heat due to the resistance effect.
Basic structure and components of electric heating tube
Electric heating tubes are usually composed of the following key parts:
-
Metal pipe: as the shell of the heating element, it is generally made of materials with high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and good heat transfer performance, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, titanium, copper and so on. Stainless steel is often the material of choice because of its excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
-
Electric heating wire (heating body) : placed inside the metal tube, is the part that actually generates heat. Electric heating wires are usually made of high resistivity alloys, such as iron chromium aluminum alloy (economical, high temperature resistance) or nickel chromium alloy (higher price but good oxidation resistance, good flexibility). The winding mode of the electric heating wire can be spiral, wavy, U-shaped, etc., to adapt to different heating needs and space constraints.
-
Filling material: The gap between the electric heating wire and the metal tube wall is filled with materials with excellent thermal conductivity and insulation properties, such as crystalline magnesium oxide powder. This powder can not only effectively transfer the heat generated by the heating wire to the pipe wall, but also play an insulating role to prevent short circuit between the heating wire and the metal shell.
-
Insulator: Used to isolate the two ends of the heating wire and the metal tube to ensure electrical insulation and prevent the current from flowing directly through the metal shell.
-
Sealing material: Used to seal the ends of the metal tube to prevent leakage of the filling material and may contain an outlet rod (wiring rod) to connect the power supply to the heating wire.
-
Metal casing (if available) : In some applications, electric heating tubes may also have an additional metal jacket layer to provide additional protection or heat dissipation.
-
Terminal: The two ends of the electric heating tube are usually equipped with terminal terminals or leads for easy connection to an external power supply.

Electric heating tube power calculation and current calculation formula
The calculation of electric heating tube power mainly depends on the following two formulas:
1. Power calculation by voltage and current (P = UI) When the voltage (U) and current (I) of the electric heating tube are known, the power (P) can be calculated directly by the following formula:

Among them:
-
Power (P) is usually expressed in watts (W).
-
The voltage (U) is measured in volts (V).
-
The current (I) is expressed in amperes (A).
2. Calculate power by voltage and resistance (P = U^2/R) If the resistance (R) and working voltage (U) of the electric heating tube are known, but the current is unknown, the following formula can be used to calculate power:
Among them:
-
Power (P) is still measured in watts (W).
-
The voltage (U) is still measured in volts (V).
-
Resistance (R) is expressed in ohms (Ω).
For the calculation of current (I), when power (P) and resistance (R) are known, the power formula in Ohm's law can be deformed to obtain the current formula:
Or when the voltage (U) and resistance (R) are known:
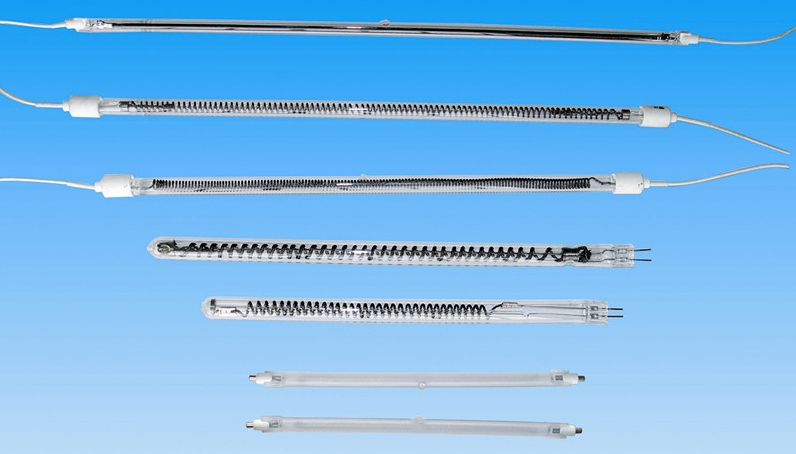
Classification and type of electric heating tube
Electric heating tubes can be classified according to different design parameters, structural forms, application scenarios, etc. :
1, resistance electric heating tube
Single head electric heat pipe
Single-head electric heat pipe, also known as single-end outlet electric heat pipe, is composed of metal tube, resistance wire and insulating filler. One end is closed, the other end is out, and the current is introduced into the resistance wire through the power lead to generate heat. The single-head electric heat pipe is compact and suitable for occasions where space is limited or local centralized heating is required, such as small ovens, laboratory equipment, mold heating, etc.
Double head electric heat pipe
Both ends of the double-headed electric heat pipe are provided with terminals, which are easy to be installed on a fixed bracket or directly inserted into the heating hole. Due to the heat dissipation at both ends, its heating uniformity is better than that of a single-head electric tube, which is suitable for a large range of uniform heating needs, such as large ovens, oil drum heaters, air heaters, etc.
2, finned electric heating tube
Finned electric heating tube is to add fins (metal sheets) outside the ordinary resistance electric heating tube to increase the heat dissipation area and improve the heat exchange efficiency. This kind of heating tube is suitable for the environment requiring rapid heating and efficient heat transfer, such as air conditioning auxiliary heating, air duct heating, liquid heater, etc. The fin material is usually aluminum or stainless steel to take into account thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
3, flange type electric heating tube
The flanged electric heating pipe is firmly connected with the equipment through the flange, which is often used for heating pressure vessels, reactors and pipeline systems. It is characterized by strong sealing, high pressure, easy installation and maintenance, especially suitable for the heating needs of high temperature, high pressure or corrosive media.
4, ceramic electric heating tube
Ceramic electric heating tube adopts alumina ceramic as the shell material, embedded resistance wire and filled with insulating medium. Ceramic material has good insulation properties and high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, making this kind of heating tube widely used in chemical, medical, laboratory and other fields with high safety and cleanliness requirements, such as electric heating plate, disinfection cabinet, experimental furnace and so on.

5, silicone rubber electric heating tube
Silicone rubber electric heating tube is made of silicone rubber wrapped resistance wire, excellent flexibility, can be bent into various shapes, to adapt to complex curved surface heating needs. At the same time, silicone rubber has good waterproof, moisture-proof and low-temperature resistance, and is often used in outdoor equipment, pipeline antifreeze, medical equipment and other occasions that require flexible and safe heating.
6, quartz glass electric heating tube
The quartz glass electric heating tube uses the characteristics of high purity, high temperature resistance and good light transmission of quartz glass, embedded tungsten wire or carbon fiber heating element, and generates infrared radiant heat after being energized. This kind of heating tube is mainly used for infrared heating equipment, such as food dryers, paint curing furnaces, physiotherapy equipment, etc., with the advantages of fast heating speed, high thermal efficiency, no open flame, no pollution and so on.
7, PTC automatic temperature electric heating tube
The Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) automatic temperature electric heater is equipped with a PTC thermistor as a heating element. When the temperature reaches a preset value, its resistance value increases sharply, limiting the current through, so that the output power is automatically adjusted to maintain a constant temperature. PTC electric heating tube is widely used in air conditioning, dehumidifier, heater and other household appliances as well as car seat heating, pipeline insulation and other fields, with the advantages of overheating protection, energy saving, long life.
8, electromagnetic induction heating tube
Electromagnetic induction heating tube uses electromagnetic field to generate eddy current heating of metal tube itself, without contact with resistance wire, no open flame, no radiation, high safety. Mainly used in industrial melting, chemical reactor, plastic machinery and other high-power heating occasions, as well as induction cooker, water heater and other household appliances.
9, electric film heating tube
The electrothermal film heating tube uses a special process to coat the resistance material on the surface of the substrate (such as PET, PI film) to form a heating layer, which has the characteristics of thin thickness, light weight and fast thermal response. Suitable for floor heating system, wall heating, electric heating and other large area, low power density heating needs, especially in building heating, agricultural seedlings, pet MATS and other fields have a wide range of applications.
10, carbon fiber electric heating tube
Carbon fiber electric heating tube adopts carbon fiber material as heating element, which has the advantages of rapid heating, high thermal efficiency, long life, energy saving and environmental protection. Suitable for all kinds of industrial and civil heating equipment, such as infrared heaters, sauna rooms, car seat heating, pipeline heating and so on.

Apply
Electric heating tubes are widely used in many fields:
-
Industrial equipment: such as various saltpeter tank, water tank, oil tank, acid and alkali tank heating, fusible metal melting furnace, air heating furnace, drying furnace, drying oven and so on.
-
Household appliances: hot water or air heating components in household appliances such as water heaters, electric kettles, electric ovens, coffee makers, dishwashers, etc.
-
Medical equipment: heating components in laboratory instruments, disinfection cabinets, medical steam generators and other medical and scientific equipment.
-
Building heating: heating elements in floor heating and piping tracing systems.
-
Others: hot pressing mold heating, food processing equipment, chemical reactor heating, agricultural seedling insulation, aerospace thermal control system, etc.
How to measure the quality of electric heating tube
Measuring the quality of an electric heating tube usually involves the following steps:
Appearance inspection:
Check whether the external tube body of the electric heating tube has obvious deformation, damage, crack, corrosion, oxidation, peeling and other phenomena.
Observe heating elements (such as resistance wires) for exposure, loosening, breakage, or severe scaling.
Check whether the wiring terminals are intact, the connection parts are tight, and the insulation sheath is intact without signs of aging.
Resistance measurement:
Use the resistance (ohm) of a multimeter to measure:
Set the multimeter to the appropriate resistance gear (such as a lower ohm gear, such as 1Ω or 10Ω, depending on the nominal resistance value of the electric heating tube) to ensure good contact with the pen.
Disconnect the power supply and ensure that the electric heating tube is in a non-charged state.
Measure the resistance value by touching the two terminals of the electric heating tube.
Under normal circumstances, the resistance value of the electric heating tube should be in the range of several hundred ohms to several thousand ohms, depending on its design power and material specifications. The resistance value of the electric heat pipe with higher power may be smaller. If the resistance value is zero or infinite, or is very different from the rated resistance value marked on the nameplate, it may indicate that the heating tube is open or short circuited, that is, there is a fault.
Insulation resistance measurement:
Check the insulation performance of the heating tube using the high resistance level of the multimeter (such as megohm) :
Set the multimeter to the appropriate insulation resistance setting (such as 10MΩ or higher).
Disconnect the power supply and ensure that the electric heating tube is not charged.
One pen touches the metal housing or ground end of the electric heating tube, and the other pen touches the wiring terminal of the heating element.
Under normal circumstances, the insulation resistance between the heating tube housing and the internal heating element should be very high, usually shown as "∞" (infinity) or a very large value (such as a few megaohm or more). If the insulation resistance value measured is low (such as only tens of thousands of ohms or even lower), it indicates that the insulation layer of the heating tube may have been broken down or seriously deteriorated, and there is a risk of leakage.
Leakage current detection (optional) :
For situations with high requirements, a special leakage current tester can be used to detect whether there is leakage in the electric heating tube.
Connect and test according to the instrument operating manual to determine if there is leakage current that exceeds the safety standard.
Functional testing (when available) :
Under the premise of ensuring safety, connect the power supply with the appropriate voltage and run according to the rated power for a period of time.
Observe whether the heating tube can heat normally, whether the temperature is uniform, and whether there is abnormal sound or odor.
Use a clamp ammeter to monitor the actual working current and compare it with the theoretical calculated value to confirm whether it is within a reasonable range.
Tip: If any abnormality is found, stop using the device and replace it in time to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the device. Be sure to follow the electrical safety operating procedures during measurement to prevent electric shock accidents.