Essential for electronic engineers: Detailed classification and application examples of active components
2024-07-26 15:16:42 458
Previously we have understood the passive components in electronic components [passive component types: classification and characteristics from inductors to crystal oscillators], today we continue to understand the active components in electronic components.
An active component (also called an active component) is an electronic component that provides gain (amplification), switching function, signal processing, or energy conversion in an electronic circuit. These components themselves require external energy to work and can play a controlling or regulating role in the circuit. So what are the categories of active components? Take a look at INFINITECH below.
1. Transistor

Bipolar transistor (BJT)
The NPN transistor consists of three layers of semiconductor material, with a P-type material in the middle and an N-type material on both sides. The larger current between the collector and emitter is controlled by a small change in the base. Suitable for amplifiers, switches, etc.
PNP transistors, in contrast to NPN, are composed of three layers of semiconductor material, with N-type material in the middle and P-type material on both sides. Similar to NPN, but the current goes in the opposite direction. Also used in amplifiers, switches, etc.
Field-effect transistor (FET)
Junction field-effect transistors (JFET) use a PN junction to control current. The current between the source and drain is controlled by changing the grid voltage. High input impedance for low noise amplifiers.
An insulated gate type field-effect transistor (MOSFET) has an insulating layer between the gate and the semiconductor. The grid voltage controls the conductive channel between the source and drain. High input impedance, low power consumption, high speed. There are also enhanced MOSFETs (when the gate voltage is higher than the threshold voltage to turn on) and depletion MOSFETs (even if there is no gate voltage, the gate voltage can adjust the degree of turn-on).
Insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) combine the advantages of MOSFETs and BJTS. Use MOSFET to control the working state of the BJT. It is characterized by high input impedance, high power processing capacity and low saturation voltage. Suitable for power conversion, motor drive, etc.
A Darlington transistor is two transistors connected in series. It has the characteristics of high gain and low speed. Application in amplifier circuit, high current drive.
Avalanche photodiodes (APDs), although not conventional transistors, are sometimes mentioned because of their amplification capabilities. Amplification of light signal by avalanche effect. It is generally used in optical receivers in optical fiber communication systems.
Silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) is composed of four layers of semiconductor material. Once switched on, it will continue to be switched on unless the power supply is disconnected or the current drops below the maintenance current. Suitable for AC power control, DC power conversion, etc.
2. Diode

Ordinary diodes are the most basic diodes and have unidirectional conductivity. Generally used in rectifier, protection circuit.
Rectifier diodes are used to convert alternating current to direct current and can withstand large currents. It is suitable for rectifier bridge and charging circuit in power supply circuit.
Fast recovery diodes have faster reverse recovery times compared to standard rectifier diodes and are suitable for high frequency switching applications.
Schottky diodes, characterized by low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, are suitable for high frequency applications.
Voltage regulator diodes (Zener diodes) provide a stable voltage in the reverse breakdown region and are often used to regulate voltage in circuits.
The detection diode has high detection efficiency and good frequency characteristics. It is often used in radio communication and radar signal processing.
Light-emitting diodes (leds), which emit light when forward-biased, can be used for indication, display, or lighting.
Photodiodes generate current when illuminated by light, that is, photogenerated current. Generally used in photoelectric sensors, optical communications and so on.
The capacitance value of varactor diode changes with the change of reverse voltage. Used in frequency adjustment and tuning circuits.
PIN diodes have long intrinsic layers and can be used to control high currents and high-speed switching. Generally used in RF switches, attenuators, etc.
Tunnel diodes (Esaki diodes) operate using quantum tunneling effects and exhibit negative resistance properties over certain voltage ranges. Applications in oscillators, amplifiers.
Fast Recovery diodes (FRDS) have fast recovery times for high frequency switching applications.
Switching diodes are used as switching elements in pulsed digital circuits with fast switching speeds. Generally used in digital circuit switch, pulse shaping.
The vacuum diode was an early diode, using vacuum tube technology. Radio receivers have been used less historically.
Laser diodes are similar to leds, but emit laser beams. Suitable for laser printer, optical disc drive, laser pointer, etc.
Infrared diodes are characterized by the emission or detection of infrared. Generally used in remote control, infrared communication and other places.
A thyristor rectifier is a four-layer semiconductor device that can control the on-state by triggering a signal. Generally used in AC power control, motor drive and so on.
Bidirectional trigger diode (BID), characterized by bidirectional trigger characteristics, used to trigger thyristors and so on.
High frequency diodes are specifically designed for use in high frequency circuits.
3, Integrated circuit (ICs)
Classification by function
Analog integrated circuit: Used to process continuously changing analog signals. Used in audio amplifier, signal conditioning, power management, etc.
Digital integrated circuit: Processing discrete digital signals, often used in logic operations and data processing.
Mixed-signal integrated circuits: process both analog and digital signals.
Classified by application field
Universal integrated circuit: Standard integrated circuit suitable for a variety of application scenarios. Examples include operational amplifiers, timers, comparators, etc.
Application-specific Integrated circuit (ASIC) : An integrated circuit custom-designed for a specific application. Applicable to encryption processors and network processors.
Microprocessor: Integrated circuit with central processing unit (CPU) function. Generally used in computers, embedded systems.
Memory integrated circuit: Used for data storage. For example, static random access memory (SRAM), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), flash memory, etc.
Radio frequency integrated circuits (RF ICs) : used for sending and receiving signals in wireless communications.
Power Management Integrated circuit (PMIC) : Used for power conversion and management. Such as voltage regulator, charge controller, etc.
Sensor integrated circuit: Integrated sensor function. Used in temperature sensor, pressure sensor, etc.
Display driver integrated circuit: used to control the work of the display. For example, liquid crystal display (LCD), organic light emitting diode (OLED).
Application-specific integrated circuits: Designed for application-specific applications. Such as TV, stereo, DVD player, VCR, computer and so on.
Classified by manufacturing technology
Silicon-based integrated circuits: Use silicon as a semiconductor material. Suitable for most modern integrated circuits.
Germanium based integrated circuit: Using germanium as a semiconductor material. Generally used in early integrated circuit technology.
Compound semiconductor integrated circuit: using gallium arsenide (GaAs), indium phosphide (InP) and other compound semiconductors.
Carbon-based integrated circuits: Use carbon nanotubes or other carbon-based materials. Common in the experimental stage, possible future applications.
Classification by integration
Small scale integrated circuit (SSI) : low level of integration, generally containing dozens of components. It is a simple logic circuit.
Medium scale integrated circuit (MSI) : Medium level of integration, usually consisting of several hundred components. Such as counters, registers, etc.
Large scale integrated circuit (LSI) : highly integrated, containing thousands to tens of thousands of components. Such as memory chips, microprocessors and so on.
Very large scale integrated circuit (VLSI) : The integration is very high, containing millions to billions of components. For example, advanced microprocessors, graphics processors, etc.
Extremely large scale integrated circuit (ULSI) : Extremely integrated, containing billions to tens of billions of components. Applies to the latest processor and memory technologies.
4. Photoelectric devices
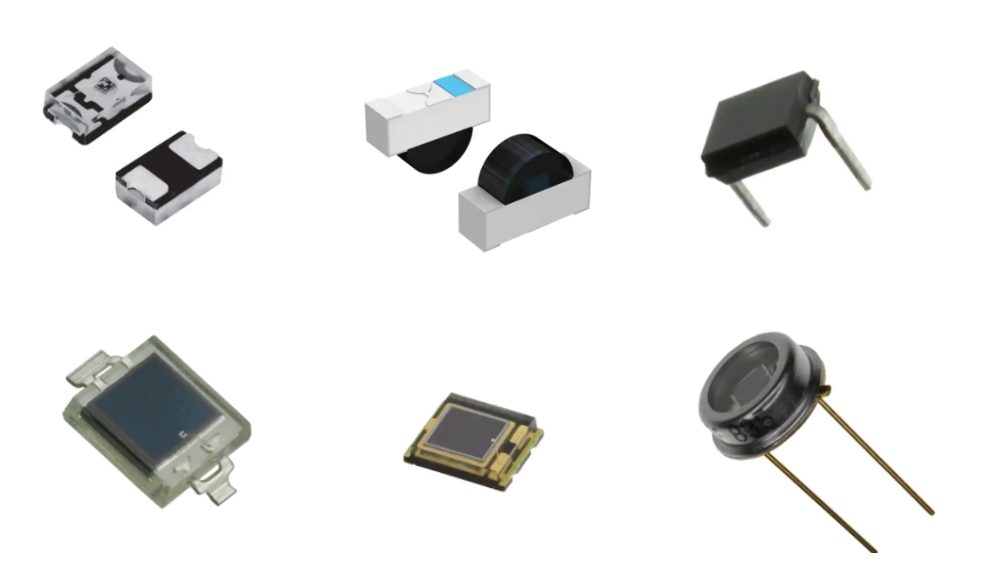

The photodiode has the characteristics of fast response, wide linear range and stable operation. Suitable for optical communication, photoelectric detection and other fields.
Phototransistor has the characteristics of high gain, high response speed and low noise. Generally used in photoelectric detection, photoelectric sensing and optical measurement.
Photoresistance is based on the photoelectric effect of photosensitive materials and is simple, easy to use and inexpensive. It is commonly used in applications such as light switches, light sensitive lamps and photometers.
Photoelectric display devices can convert electrical energy into light energy and display images or information, including organic light-emitting diodes (OLeds), liquid crystal displays (LCDS) and e-ink screens.
The photoelectron multiplier tube has the characteristics of high sensitivity, low noise and high gain.
The laser has the characteristics of good monochromism, strong directivity and fast modulation speed. Suitable for laser printing, laser cutting, laser processing and other fields.
Photocells use the photoelectric effect to convert light signals into electrical signals. Used in early photoelectric detection.
Photomultiplier tube has the characteristics of high sensitivity, low noise and high gain. It is used in high precision photoelectric measurement, low light detection and other fields.
A photocell converts light energy directly into electricity. It is used in solar panels, photoelectric detection, etc.
Optocouplers are used for electrical isolation and signal transmission.
The photodiode is based on a semiconductor material and generates a photocurrent in the PN junction region when exposed to light.
Phototransistors are similar to ordinary transistors, but light exposure changes their electrical conductivity.
5. Vacuum tube
Classification by heating method
Direct-heat vacuum tube: the cathode is heated directly through the filament, and the cathode characteristics are easily affected by the filament temperature. Suitable for early vacuum tube designs, such as some simple amplifiers and oscillators.
Side-heated vacuum tube: The cathode is heated through a side filament, and a metal sleeve helps to keep the cathode temperature stable. Suitable for circuits that require higher stability, such as high quality audio amplifiers.
Classification according to structure and use
Vacuum diode: The simplest type of vacuum tube, containing only a cathode and an anode.
Vacuum triode: A grid is added to the diode to control the flow of electrons. Applied to amplifiers and oscillators.
Tetrode: A control pole is added to the triode to provide additional control functions. Suitable for more complex amplifiers and oscillators.
Beam tetrode: An improved version of a tetrode in which the flow of electrons is confined to a narrow area.
Vacuum pentode: Add a plate to the tetrode to improve amplification performance.
Composite tube: contains multiple independent functional units, such as multiple triode or tetrode combinations. With complex circuit functions such as multistage amplifiers.
Other types
Cathode ray tube (CRT) : A special vacuum tube used to display images.
Magnetron: Vacuum tube that produces microwaves. Used in radar system, microwave oven.
Line output transformer (LOPT) Vacuum tube: line scanning circuit used in televisions. It was used in early television receivers.
Special purpose vacuum tube
Frequency multiplier tube: Used to produce higher frequency signals.
Modulator tube: Used to modulate signals. Examples include radio and radar systems.
Amplifier tube: Used for signal amplification. Such as audio amplifier, radio receiver.
Oscillating tube: Used to produce a stable oscillating signal. Used in oscillator, clock generator.
Container structure classification
Glass vacuum tube: the most common type, using glass tube encapsulation. Widely used in various electronic equipment.
Vacuum tubes of metal: for applications requiring greater durability and reliability. Used in military equipment, industrial applications.
6. Power management chip
Linear voltage regulator: simple structure, stable output voltage, low noise during operation. The efficiency is relatively low, especially when the voltage difference between input and output is large. Suitable for battery powered small electronic devices, such as handheld devices, sensors, etc.
Switching regulator: High efficiency, especially at large voltage differences. It can realize a variety of modes such as boost, buck and reverse. Some electromagnetic interference (EMI) will be generated during operation. Applications that require high efficiency power conversion, such as laptop adapters, server power supplies, etc.
DC-DC converter: including Buck (Buck), Boost (Boost), buck-boost (Buck), Inverting (Inverting), etc. Efficient and compact. It is suitable for various application scenarios that require voltage transformation.
LED driver: can control the current or voltage of the LED. Provides constant current or voltage output. Used in LED lighting system, display backlight.
Battery charging management chip: supports a variety of charging algorithms, such as trickle charging, constant current charging, constant voltage charging, etc. Can integrate overcharge, overdischarge, overheat protection and other functions. Suitable for portable equipment, electric vehicle battery management system, etc.
Fuel metering chip: Used to monitor battery status, including remaining power, health status, etc. Provides accurate battery life prediction. Applied to smart phones, laptops and other portable devices.
Power monitoring chip: monitor the voltage, current, temperature and other parameters of the power system. Provides fault reporting and diagnosis functions. Applicable to data centers, servers, industrial control systems, etc.
Power sequencer: Controls the turn on sequence of multiple power supplies to prevent transient voltage shocks. Soft start and soft close can be implemented. Used in server, embedded system, etc.
Power switch: Controls the power supply. It can integrate overload protection, short circuit protection and other functions. Suitable for power management in various electronic devices.
Timing controller: Controls the startup and shutdown sequence of components in the power system.
Pulse width modulation controller: Used to control the switching frequency and duty cycle of the switching regulator. Achieve efficient power conversion. Used in power adapter, switching power supply, etc.
Multiphase controller: Supports multiphase power supply to improve load balancing capability. Reduce power ripple and improve power efficiency.
Integrated Power Module: The various components needed for power management are integrated into a single package. Simplify design and improve reliability. It is suitable for space-limited application scenarios, such as mobile devices and wearable devices.
Thermal management chips: Monitor and control the temperature of equipment. Overheat protection can be integrated.
Magnetic resonance charging chip: Support wireless charging standards, such as Qi standard. Contact or non-contact wireless power transmission can be achieved.
In addition to the above common active components, there are some other active components, such as thyristor rectifiers, relays and so on. By the way, if you have component information inquiry and procurement needs, please click to visit INFINITECH.